February 17, 2016
A new study by the Brookings Institution finds that the inequality in life expectancy is growing more pronounced—and at a faster rate—between rich and poor Americans, Citylab reports.
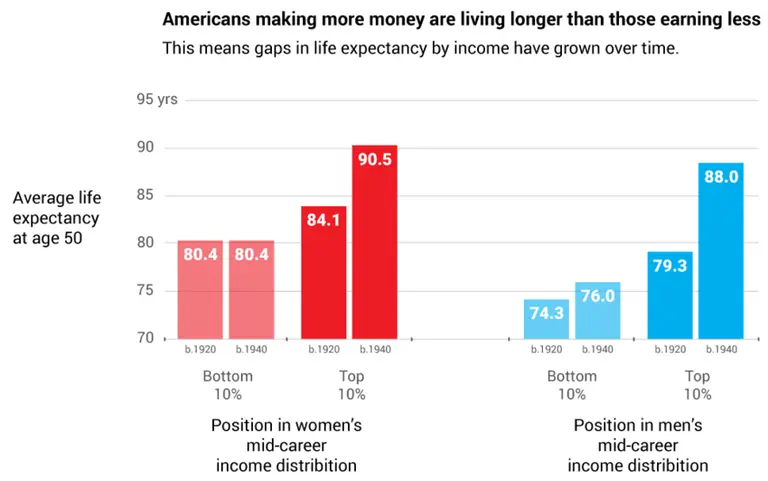
The study, based on government records and Social Security data, found that for men born in 1920, the average life expectancy at 50 was 79 years if he was in the top ten percent of the income spectrum; for the lowest 10 percent, that fell to 74 years (a five-year difference). Forwarding to men born in 1940, that gap widens to a 12 year difference with the top 10 percenters living until 88 on average, compared to 76 for the bottom 10. For women, the same gap grew from four to 10 years over the same time span.
Find out more